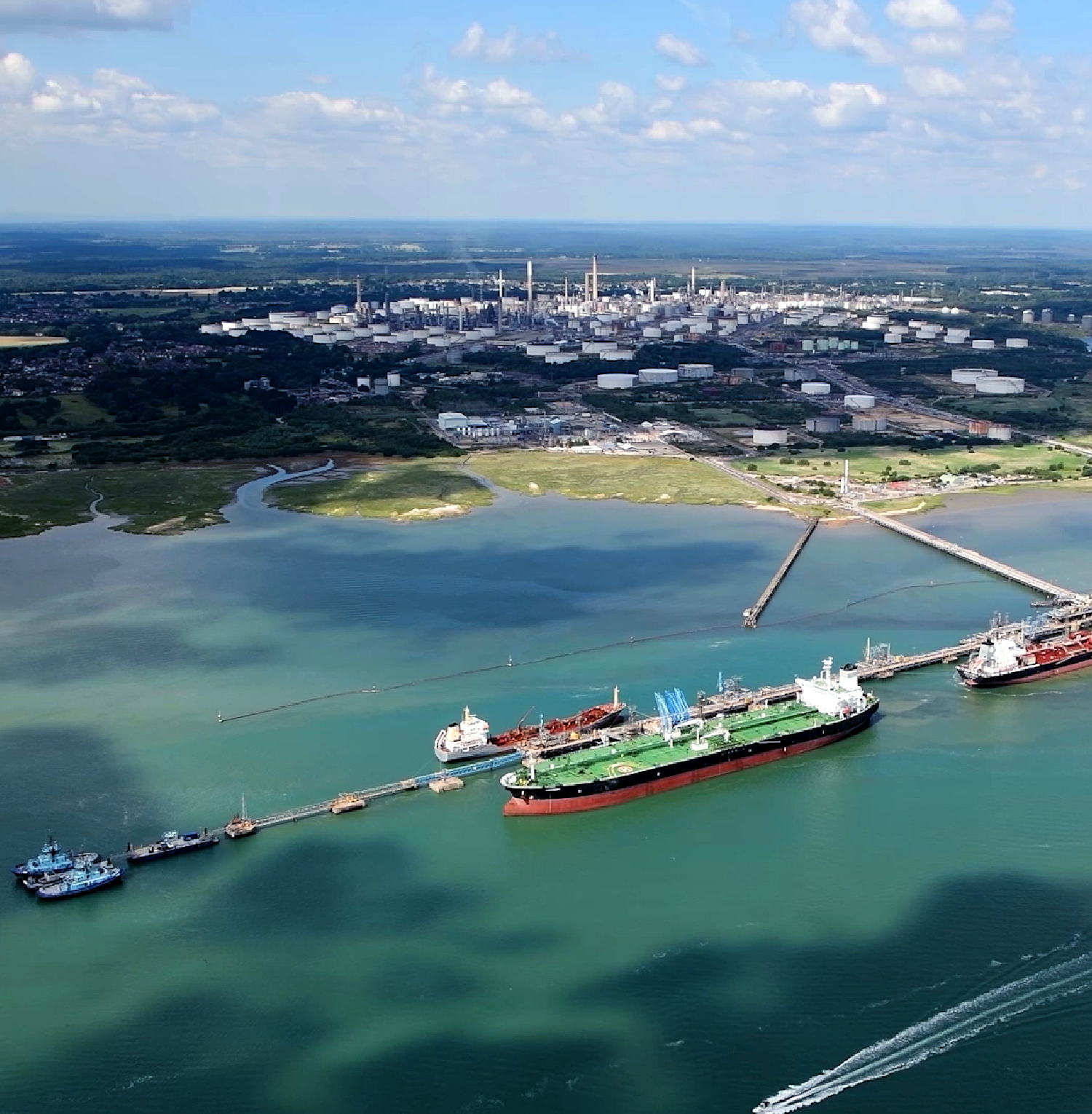
What’s happening: ExxonMobil has signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) with gas distribution company SGN and Green Investment Group (GIG) to look at ways to lower industrial CO2 emissions in the Southampton (U.K.) area, including at the company’s Fawley (U.K.) complex, using low-carbon, or “blue,” hydrogen.
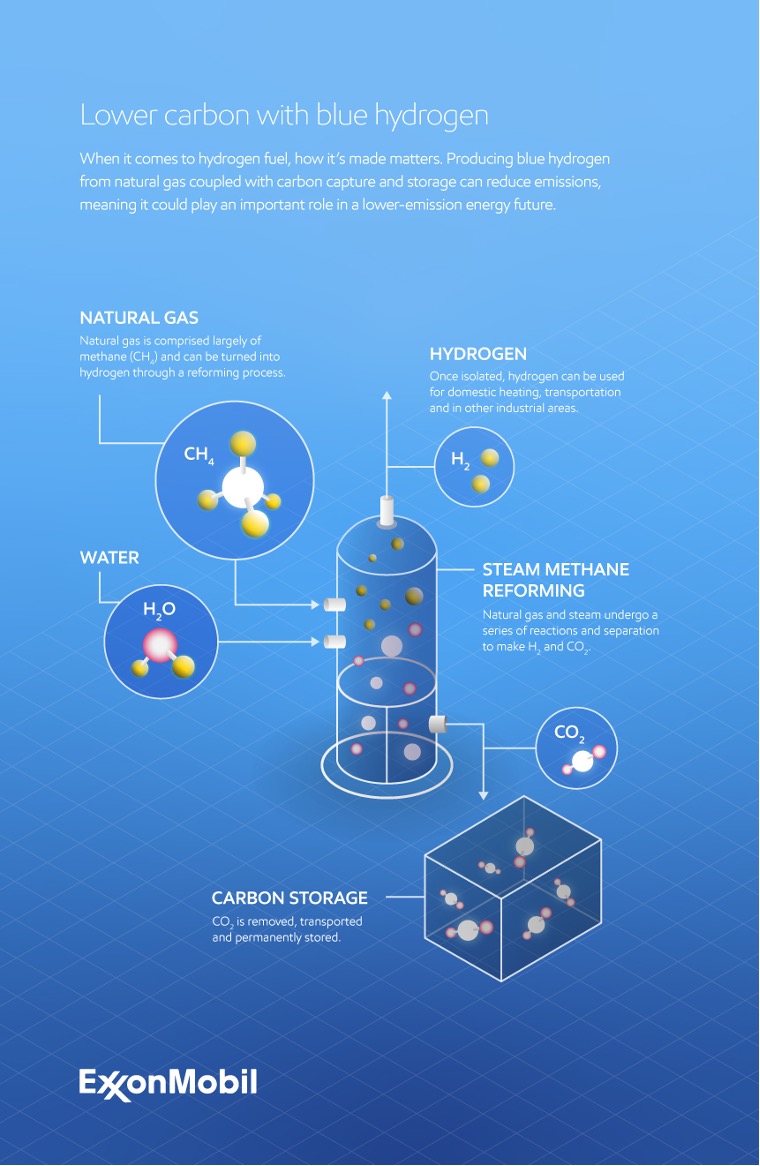
Blue hydrogen is a term often used to refer to hydrogen that has been manufactured from natural gas with carbon capture and storage technology capturing the associated CO2 emissions from the process.
If the technical and business feasibility of the initiative is confirmed, a facility to capture industrial CO2 emissions could be constructed near the Southampton Water industrial cluster in southern England. The captured CO2 would then be shipped offshore for safe and permanent storage.
The production of hydrogen could, in such a scenario, begin as early as 2030. Initial projections from the study identify that carbon capture and storage facilities associated with the hydrogen production could capture nearly 2 million tonnes of CO2 per year, while potentially producing more than four TWh of hydrogen annually.
Why it matters: The potential of this initiative could increase the use of hydrogen, which may help decarbonise the area’s industrial sector. Hydrogen would be delivered to customers to help reduce emissions from domestic heating, industrial processes and transportation, and CO2 would be captured and shipped to a secure offshore storage location. This could also attract significant investment in the community, support existing employment, and stimulate the creation of local jobs.